Clover Weed

What Is Clover Weed?
Clover weed, also called Trifolium spp., is a common weed found in lawns and gardens. It grows well in poor soil, especially where nitrogen levels are low. Clover often spreads in areas with nutrient problems. Interestingly, it’s sometimes added to lawn mixes because it can help improve soil by adding nitrogen.
Characteristics of Clover Weed
-
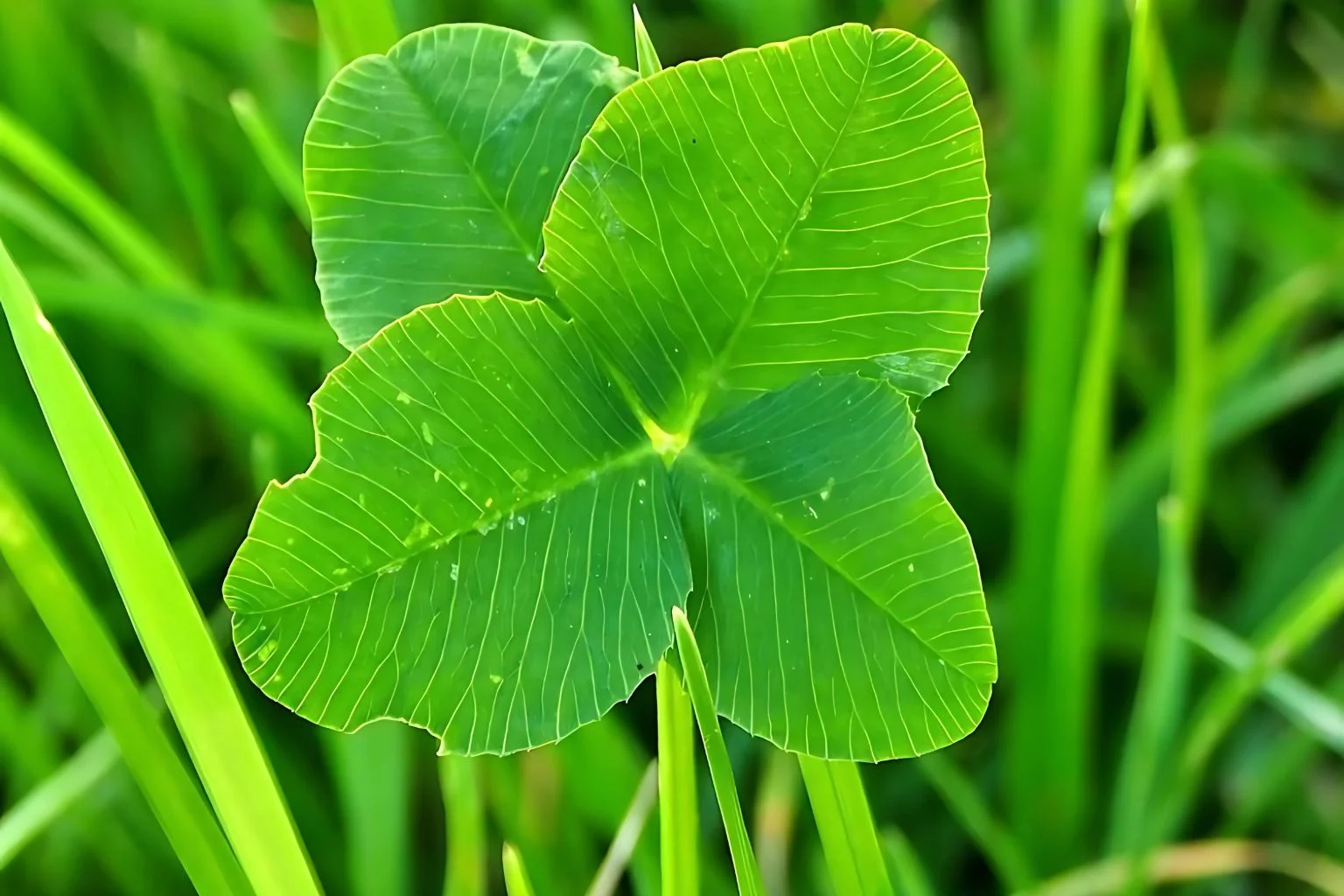
Appearance: Clover weed typically grows as a low-lying, spreading plant with trifoliate leaves.
-
Leaves: The leaves are trifoliate, meaning they have three leaflets, often with a distinctive white or pink flower.
-
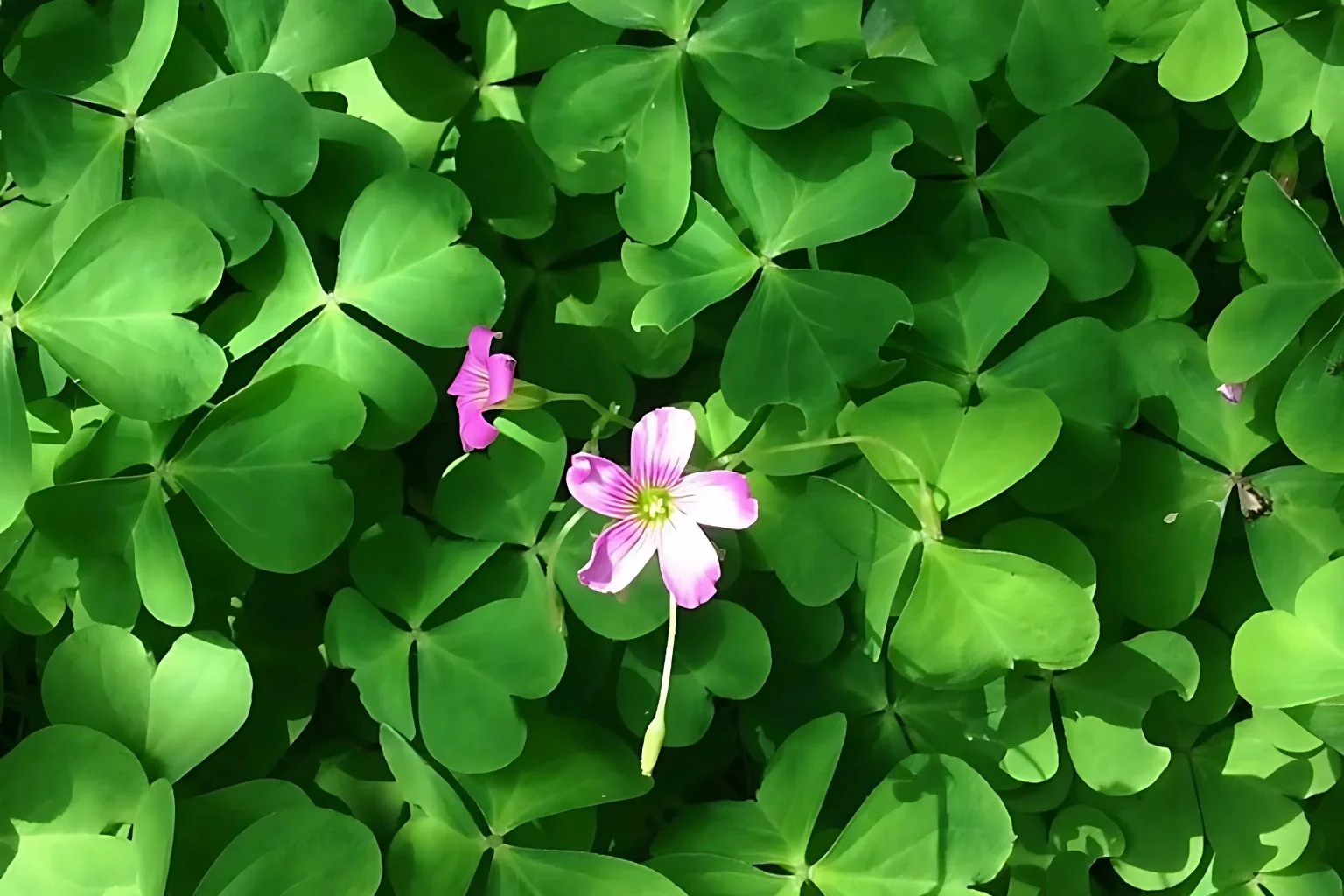
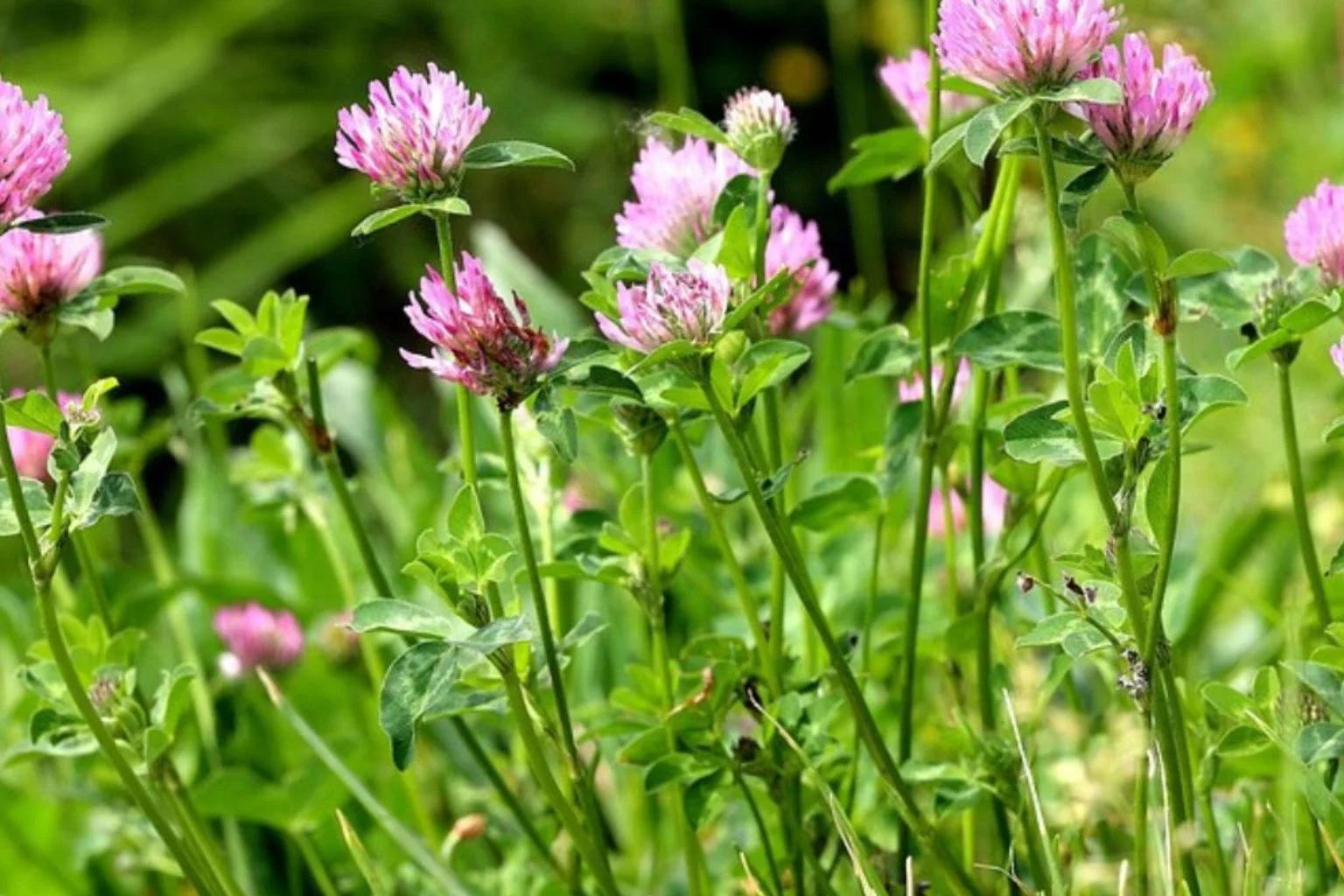
Flowers: It produces small white or pink flowers, which are a distinguishing feature.
-
Growth Habit: It can grow quite aggressively, outcompeting native vegetation and other crops.



Why Is It A Problem?
Clover weed is a problem because it competes with lawn grass for nutrients and water, potentially reducing lawn quality and disrupting its uniform appearance. Additionally, clover can host pests and spread seeds easily, making it challenging to manage.
Environmental Impact
-
Nitrogen Fixation: As a legume, clover can fix atmospheric nitrogen, enriching the soil but potentially altering nutrient balances.
-
Habitat Alteration: In natural habitats, clover can alter native plant compositions by outcompeting native species.
Agricultural and Pastoral Impact
-
Pasture Quality: While clover can improve pasture quality by adding nitrogen, it can also reduce the diversity of desirable grasses.
-
Land Use Limitations: Dense clover growth can limit land use for grazing or other agricultural purposes.
How to Identify Clover Weeds
You can esily identify lover weeds by their distinctive features:
-
Leaves: Clover has trifoliate leaves, meaning each leaf is composed of three leaflets. These leaflets are typically green with a white crescent-shaped mark or a pale green ‘V’ shape on each leaflet. The edges of the leaflets are lightly serrated, and there is a visible vein along the middle.
-
Flowers: Clover produces small, globe-like flowers in various colors such as white, pink, red, yellow, or purple. These flowers are densely formed on upright stalks and bloom from winter to summer.
-
Growth Habit: Clover spreads horizontally through stolons, forming a dense mat of foliage. It is a perennial plant that presents itself all year round.
Effective Methods
For effective clover weed control, a combination of methods can be employed. Herbicides are a potent tool, with selective herbicides being particularly effective. These products, such as Searles Bindii & Clover Killer and Yates Weed’n’Feed, target clover while sparing grass, making them ideal for lawn management. It’s crucial to apply herbicides during the active growing season for optimal results. You can also consider the ways below:
Clover Weed Control
Controlling clover weed involves a combination of cultural practices and targeted treatments.
-
Cultural Practices: Maintain a well-fertilized lawn with adequate nitrogen levels to discourage clover growth. Adjust mowing heights to block sunlight from reaching clover.
-
Mechanical Control: Hand-pulling or using tools to remove clover, ensuring all roots are removed.
-
Chemical Control: Use selective herbicides that target broadleaf weeds without harming grass.
-
Natural Remedies: For small areas, boiling water or vinegar mixed with dish soap can be effective.
Early intervention is crucial to prevent clover from spreading extensively. Regular lawn maintenance and strategic control methods can help manage clover weed effectively.











 Mosquito Traps
Mosquito Traps