White Clover

What Is White Clover?
White clover is a common plant that grows in lawns, pastures, and gardens. It has three round, green leaflets and small white flowers that often have a pinkish tinge. People sometimes like white clover because it adds colour and helps improve soil by adding nitrogen. However, it can spread quickly and take over lawns or pastures if you don’t manage it properly.
Characteristics of White Clover
White clover is a low-growing weed that spreads quickly in lawns, gardens, and paddocks. It’s easy to spot once you know what signs to look for.
Leaves
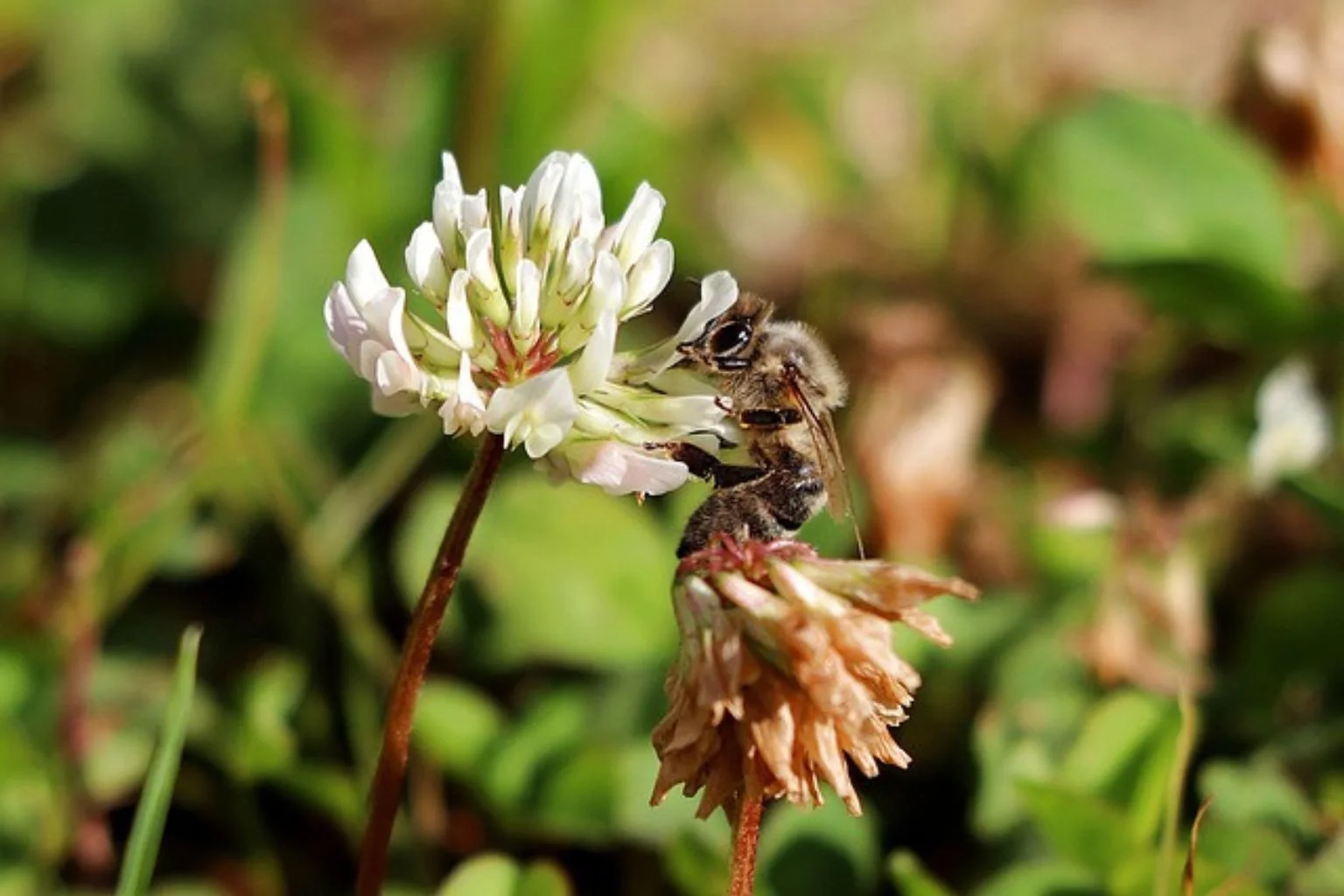
To start, white clover has small, round leaves grouped in sets of three. Each leaflet may have a pale mark shaped like a crescent. The leaves grow close to the ground, helping the plant stay hidden among grass.
Flowers
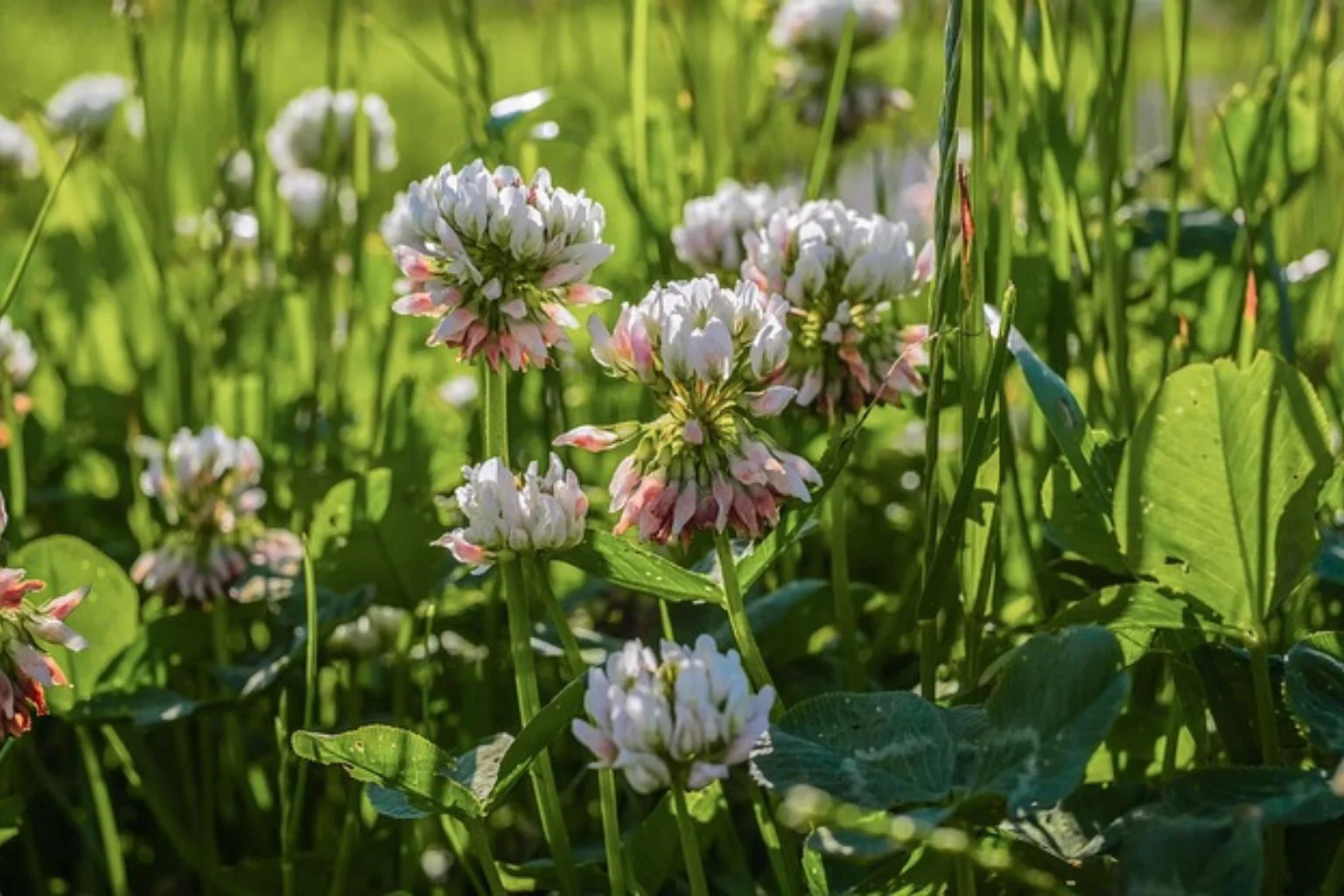
Next, the flowers are small, white, and form in tight, round clusters. They grow on short stalks just above the leaves. As they age, the flowers may turn a light pink or cream colour.
Seeds
As the flowers dry out, they turn into seed heads. These seeds are tiny and spread easily through mowing, foot traffic, or wind—making the weed hard to stop once it starts.
Stems
The stems are thin and creep along the ground. They often root at the joints (where the leaves meet the stem), allowing new plants to grow quickly from each point.
Roots
White clover has shallow roots, but they spread wide. Since the stems root as they go, the plant forms a thick mat that takes over patches of lawn or soil.
Growth Habit
Overall, white clover grows in a low, spreading way. It thrives in thin or patchy grass and likes sunny spots with moist soil. Once established, it can be tricky to remove without the right treatment.



Why Is It A Problem?
How to Identify White Clover
-
Leaves: White clover has three round leaflets with a faint white mark on each. The leaves grow close to the ground on short stems.
-
Flowers: It produces round clusters of small white flowers, sometimes with a pinkish tint. The flowers bloom mostly in spring and summer.
-
Growth: White clover spreads by sending out runners (stolons) that root at the nodes, helping it cover large areas fast.
How to Identify White Clover
White clover can crowd out grass and other plants in your lawn or pasture. It grows fast and forms thick patches that change the look and feel of your lawn. Also, because it fixes nitrogen in the soil, it can encourage weeds that like richer soil to grow. If you want a pure grass lawn, white clover can be a weed you need to control.
Effective Methods
Keep Your Lawn Healthy
Start by growing strong, healthy grass. Mow regularly and fertilise your lawn to give grass the nutrients it needs. Healthy grass grows thick and makes it harder for white clover to spread.
Water Wisely
Water your lawn deeply but less often. White clover can survive dry spells better than some grasses, so watering properly helps grass stay ahead.
Remove Clover by Hand
If you spot small patches of white clover, pull them out by hand. Try to remove the roots so it doesn’t grow back. This works best when the soil is moist.
Use Selective Herbicides
For larger patches, apply a selective herbicide made for broadleaf weeds. Products with 2,4-D or dicamba work well against white clover without harming your grass. Always follow the label instructions and spray when the clover is actively growing.
Prevent New Growth
-
Remove flowers before they turn to seed to stop white clover spreading.
-
Keep your lawn thick and healthy to block clover seedlings.
-
Check your lawn regularly and remove new clover plants early.











 Mosquito Traps
Mosquito Traps