Powdery Mildew Treatment

What Is Powdery Mildew?
Powdery mildew is a common fungal disease that affects a wide range of plants, including roses, grapes, peas, and many others. It is characterized by a white or gray powdery coating on the leaves and stems of infected plants. Powdery mildew thrives in warm, dry climates and can spread rapidly, causing significant damage to plant health and productivity. In this guide, you’ll get to know the Powdery Mildew Treatment to keep your plants healthy and thriving.
Characteristics of Powdery Mildew
-
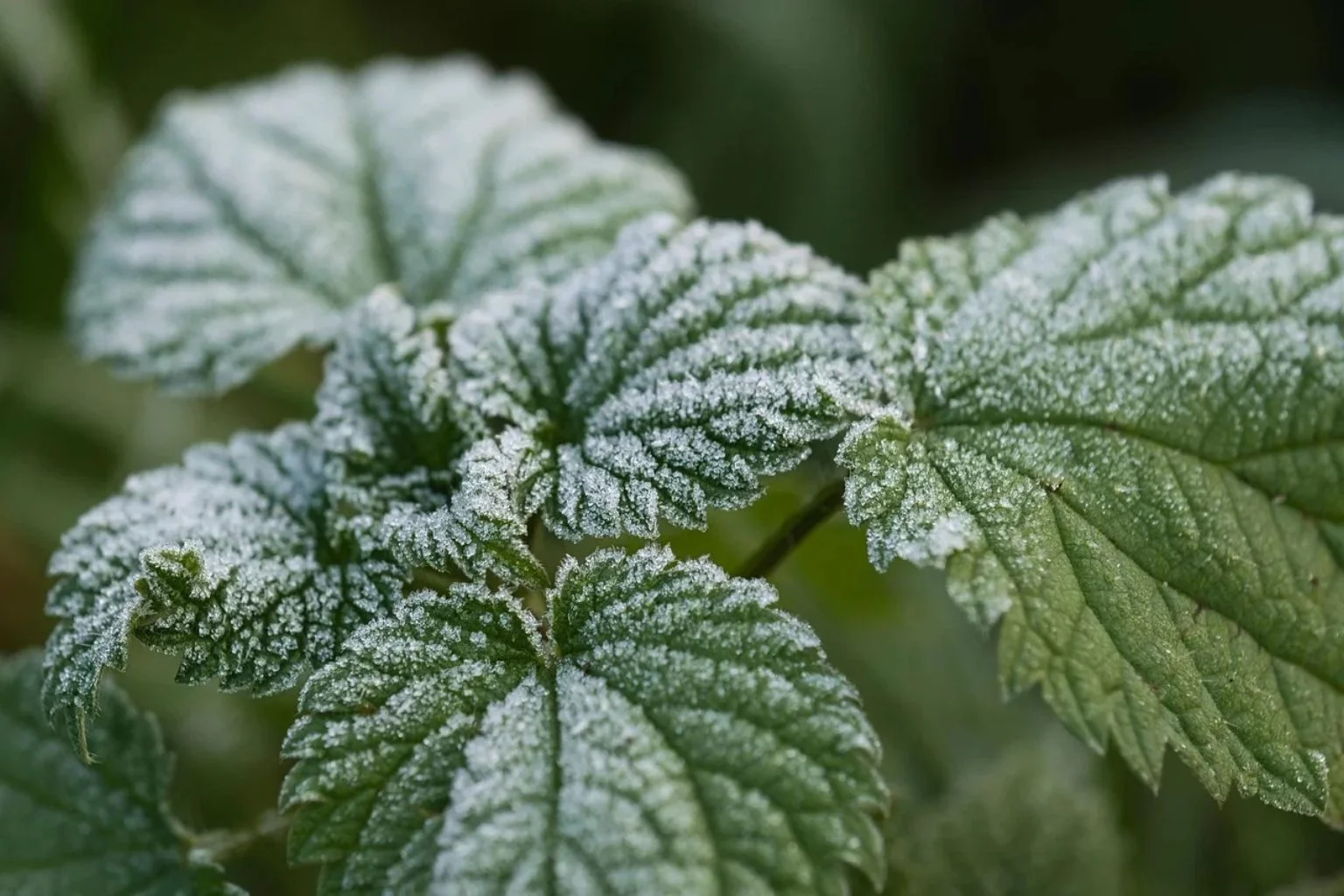
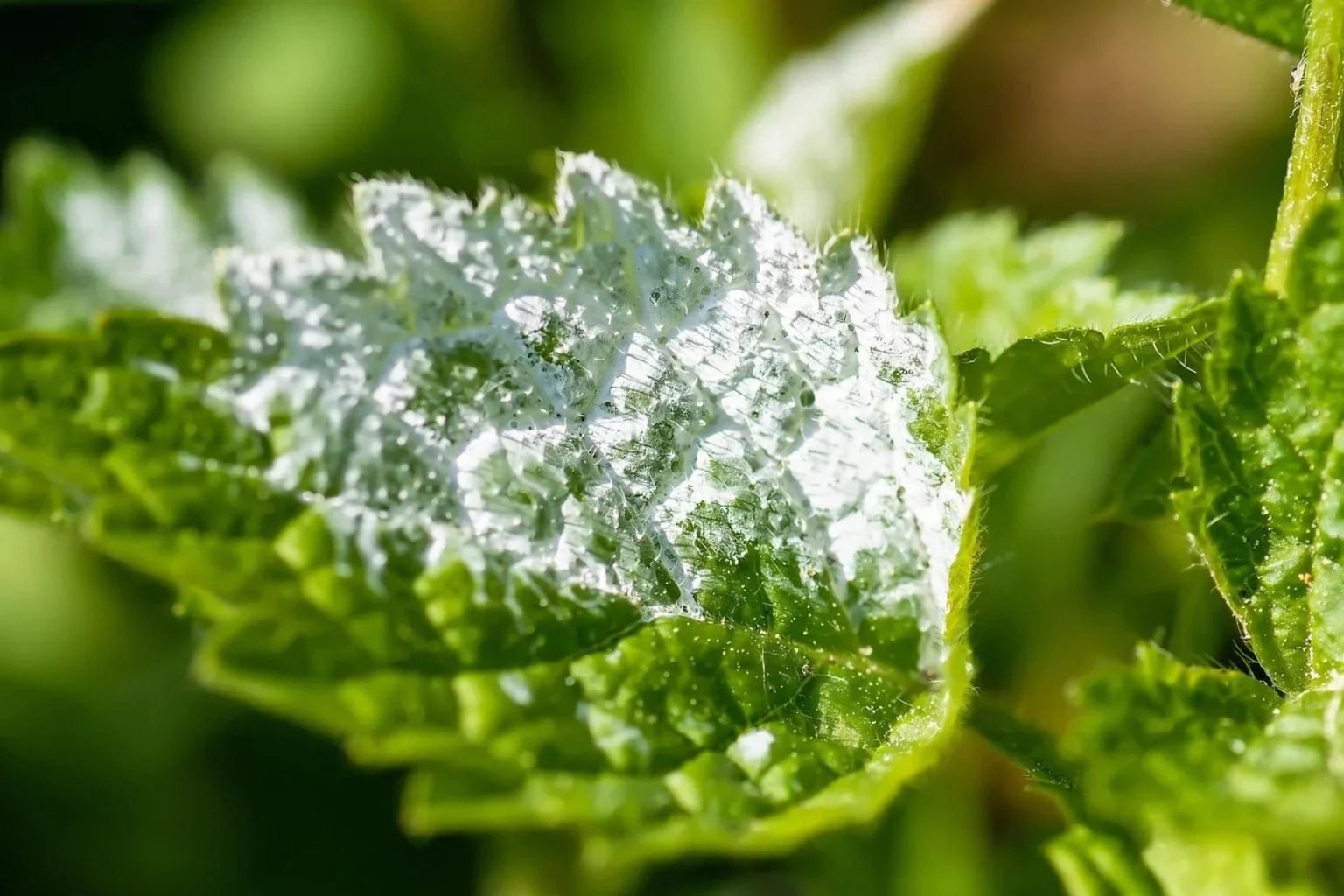
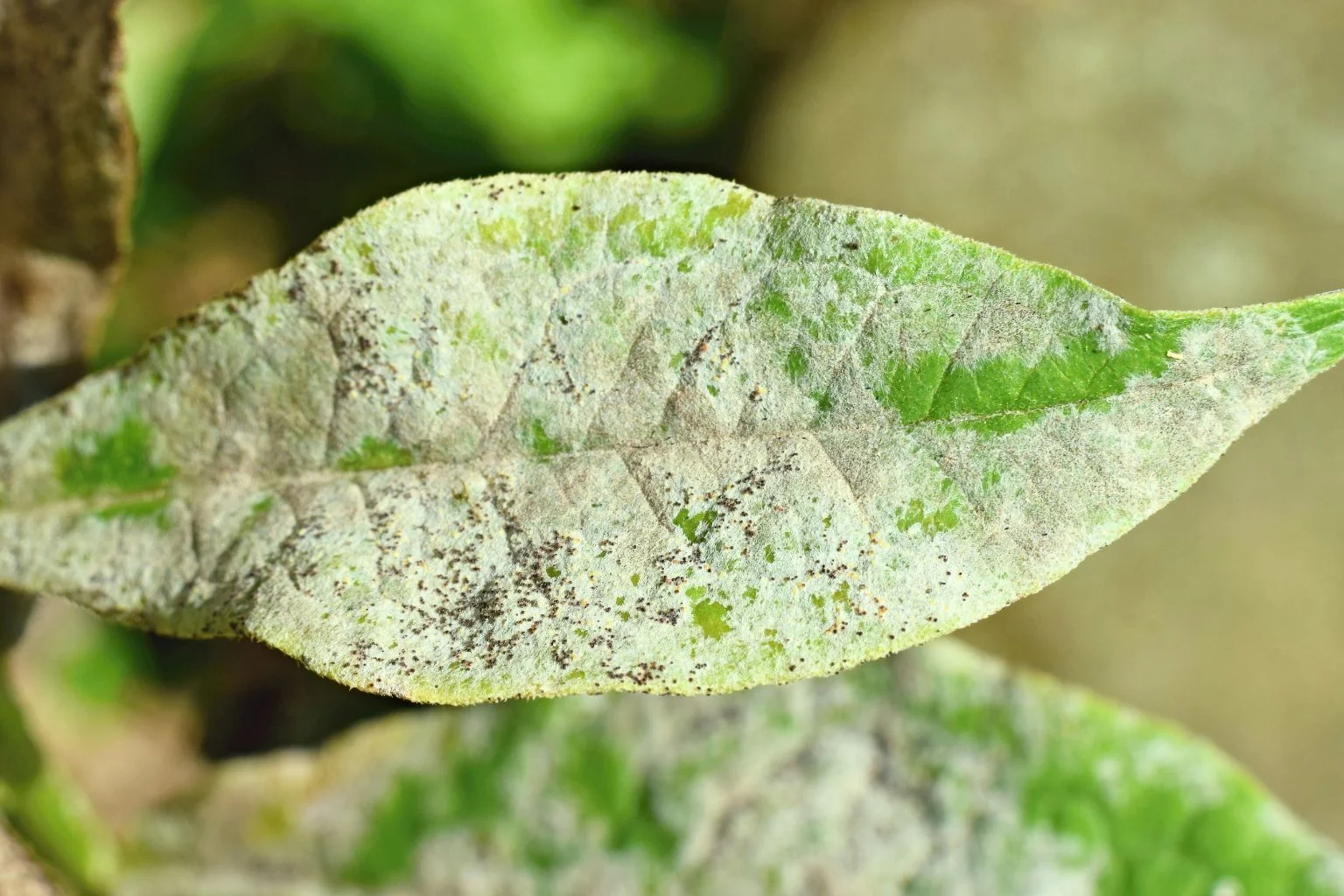
Appearance: Powdery mildew appears as a white or gray powdery substance on the leaves and stems of plants. It can distort young stems and flower buds.
-
Growth Habit: The disease spreads through airborne spores and can be exacerbated by poor air circulation and high humidity.
-
Impact: Infected tissue often withers and dies, weakening the plant and reducing its ability to photosynthesize.



Why Is It A Problem?
Powdery mildew is a plant issue because it can significantly weaken plants, reduce yields, and alter plant appearance. It can also spread quickly to other plants, making it challenging to manage in gardens and agricultural settings.
Environmental Impact
-
Plant Diversity: Powdery mildew can reduce plant diversity by favoring the growth of resistant species over susceptible ones.
-
Ecosystem Disruption: In severe cases, it can disrupt local ecosystems by altering the composition of plant communities.
Agricultural and Pastoral Impact
-
Crop Yield Reduction: Powdery mildew can lead to significant reductions in crop yields, especially in susceptible varieties.
-
Economic Impact: The disease can increase costs for farmers due to the need for fungicides and other control measures.
How to Identify Powdery Mildew
Powdery mildew is easily identified by its characteristic white or gray powdery coating on plant leaves and stems. It often appears on the upper surfaces of leaves and can be distinguished from other fungal diseases by its powdery texture.











 Mosquito Traps
Mosquito Traps